Cellular Respiration Definition
Cellular breathing is the procedure thru which cells convert sugars into electricity. To create ATP and different types of electricity to strength mobile reactions, cells require gasoline and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical procedure of turning electricity right into a useable shape.

Cellular Respiration Overview
Eukaryotes, consisting of all multicellular organisms and a few single-celled organisms, use cardio breathing to provide electricity. Aerobic breathing makes use of oxygen – the maximum effective electron acceptor to be had in nature.
Aerobic breathing is an incredibly green procedure permits eukaryotes to have complex lifestyles capabilities and lively lifestyles. However, it additionally method that they require a consistent deliver of oxygen, or they may be not able to acquire electricity to live alive.
Read Also: Principle of Beneficence in Ethics & Nursing: Definition & Examples
Prokaryotic organisms consisting of bacteria and archaebacteria can use different paperwork of breathing, that are fairly much less green. This permits them to stay in environments in which eukaryotic organisms ought to now no longer, due to the fact they do now no longer require oxygen.
Products of Cellular Respiration
ATP
The major made of any mobile breathing is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This molecule shops the electricity launched throughout breathing and permits the mobile to switch this electricity to numerous elements of the mobile. ATP is utilized by some of mobile additives as a supply of electricity. For example, an enzyme may also want electricity from ATP to mix molecules. ATP is likewise typically used on transporters, that are proteins that feature to transport molecules throughout the mobile membrane.
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a usual product created through mobile breathing. Typically, carbon dioxide is taken into consideration a waste product and should be removed. Hence, in an aqueous solution, carbon dioxide creates acidic ions. This can appreciably decrease the pH of the mobile, and in the end will motive ordinary mobile capabilities to cease. To keep away from this, cells should actively expel carbon dioxide.
Other Products
While ATP and carbon dioxide are often produced through all types of mobile breathing, distinct forms of breathing depend upon distinct molecules to be the very last acceptors of the electrons used within side the procedure.
Purpose of Cellular Respiration
All cells want a good way to acquire and shipping electricity to strength their lifestyles capabilities. Hence, for cells to keep living, they should be capable of perform vital machinery, consisting of pumps of their mobile membranes which hold the mobile’s inner surroundings in a manner that’s appropriate for lifestyles.
The maximum common “electricity currency” of cells is ATP – a molecule which shops a whole lot of electricity in its phosphate bonds. These bonds may damage the launch that electricity and result in modifications to different molecules. Hence, consisting of the ones had to strength mobile membrane pumps.
Read Also: Deletion Mutation: Definition, Examples & Diseases
Because ATP isn’t always strong over lengthy intervals of time. It isn’t always use for lengthy-time period electricity storage. Instead, sugars and fat are use as a lengthy-time period shape of storage and cells. They should continuously procedure the ones molecules to provide new ATP. This is the procedure of breathing.
Cellular Respiration
Let’s begin this lesson with a question. What did you need to devour nowadays? Or extra specifically, why did you devour nowadays? Sure, you have been possibly hungry, however from a organic foundation you had to devour a good way to acquire electricity. Your frame is based at the electricity from meals to hold you alive and healthy. The breakfast you have nowadays is damage and transforms into usable mobile electricity. Using a procedure referred to as mobile breathing. Moreover, cellular breathing is the collection of reactions that convert electricity from vitamins into adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is the number one shape of electricity cell’s use. Here’s the way it works.
Equation
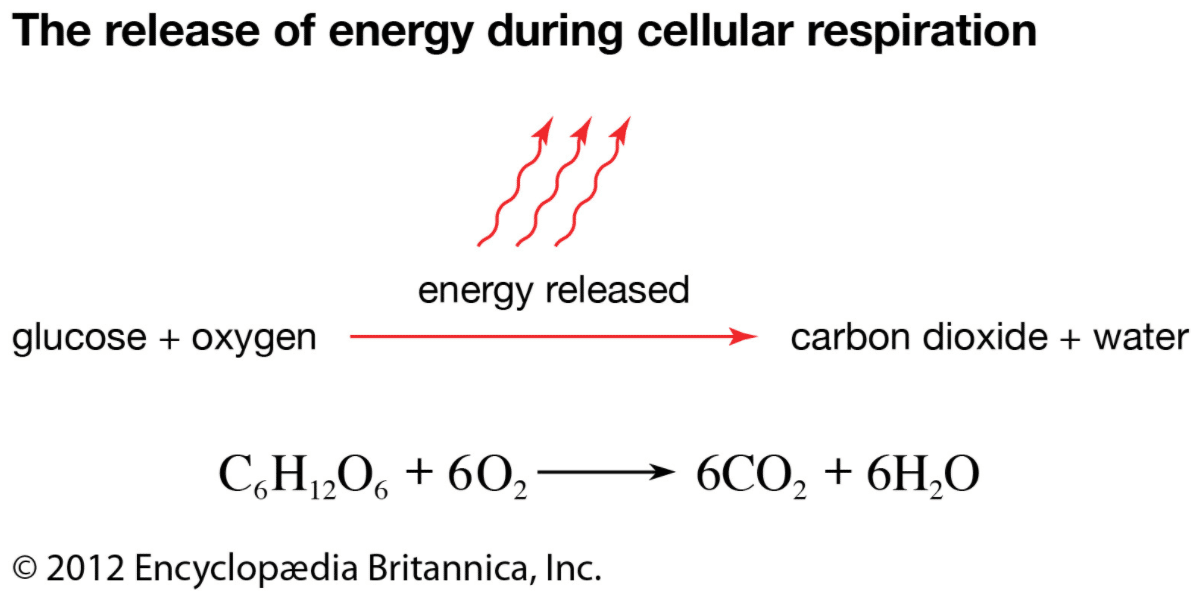
Although mobile breathing has a couple of elements, the simple chemical equation is:
Oxygen + Glucose (sugar) = Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
This equation is regularly damages elements, the reactants and the goods. Therefore, reactants are the molecules that start mobile breathing, in this example that might be oxygen and glucose. Moreover, products are what paperwork throughout mobile breathing. Here, the goods are carbon dioxide, water, and electricity. As the point of interest of this lesson is at the reactants of mobile breathing, oxygen and glucose, let’s test the ones.
Reactants
The first reactant within side the equation for mobile breathing is oxygen. Most humans are acquaint with oxygen in view that it is the number one fuel online for maintaining our lives. Hence, we acquire oxygen through truly breathing. Oxygen is noticeably reactive and consequently ideally suited for riding chemical reactions consisting of mobile breathing. However, humans can be much less acquainted with the second one reactant in our breathing equation: glucose.
Cellular Respiration Formula
Cellular respiration is a collection of metabolic procedures through which cells produce power in ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from the food particles and launch waste items. Usually, the food particle sugar (stemmed from carbs) is a metabolic fuel in cellular respiration. Yet, amino acids (derived from healthy proteins) and fats (derived from fats) can also be utilized as metabolic gas when kept glucose in our body becomes diminished.
The metabolic fuels generate energy through the three stages of cellular respiration.
Chemical Formula For Cellular Respiration
( 1) Initial stage: The first stage of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. In this phase, glucose is weakening as well as creates power using the glycolysis path. There are two kinds of glycolysis present: cardiovascular glycolysis and an additional is anaerobic glycolysis.
2) Second phase: The second phase of cellular respiration happens in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell and also participates with the Citric acid cycle (also called the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle). Oxygen is necessary for this stage. Acetyl Co-A is the substrate of the Citric acid cycle. 2 molecules of Acetyl Co-A are produced in the first stage of cellular respiration by malfunctioning one particle of glucose.
( 3) 3rd phase: The 3rd phase of cellular respiration occurs through the electron transportation chain. This chain lies in the inner mitochondrial membrane layer of the cell. In this stage, NADH and FADH2 donate electrons. These electrons pass along the electron transport chain from one carrier to one more.